

Cathode
Kellner, who in 1886 patented the use of cathode (caustic soda) and anode (chlorine) liquors in the manufacture of cellulose from wood-fibre, and has since evolved many similar processes, has produced an apparatus that has been largely used. Negative (cathode) electrode is conventionally black, and that to the positive (anode) electrode is red. An electrode is a medium that intervenes between the cable from the electrical stimulator and the recipient's body (only surface electrodes will be discussed here).
Cathode (styled as CATHODE) is an engine built by the Creative Assembly in partnership with AMD for the 2014 video game Alien: Isolation. It is a highly modified version of the engine created for an earlier title, Viking: Battle for Asgard. The trademark for Cathode's name was filed by SEGA on August 26th 2013, and eventually granted February 20th 2014. The Cathode engine was named after its.
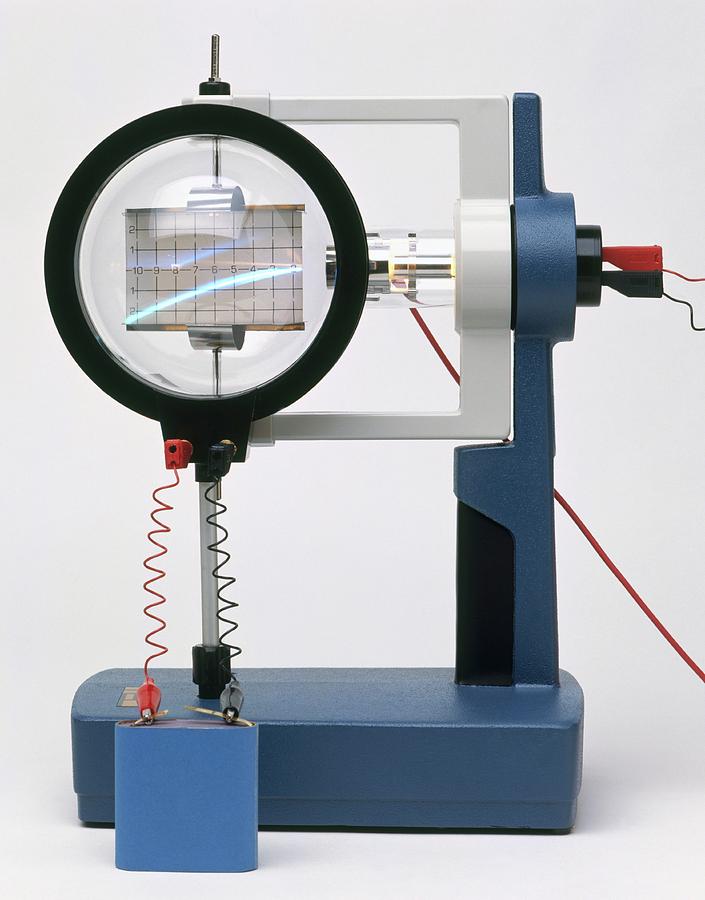
Cathode Ray Experiment

Cathode Ray
A cathode is an electrode through which electric current flows out of a polarized electrical device. The direction of electric current is, by convention, opposite to the direction of electron flow. This convention is sometimes remembered using the mnemonic CCD for cathode current departs.Cathode polarity is not always negative. Although positively charged cations always move towards the cathode and negatively charged anions move away from it, cathode polarity depends on the device type, and can even vary according to the operating mode. In a device which consumes power, the cathode is negative, and in a device which provides power, the cathode is positive:⁕In a discharging battery or a galvanic cell the cathode is the positive terminal since that is where the current flows out of the device. This outward current is carried internally by positive ions moving from the electrolyte to the positive cathode. It is continued externally by electrons moving inwards, negative charge moving one way constituting positive current flowing the other way. For example, the Daniell galvanic cell's copper electrode is the positive terminal and the cathode.
